Introduction
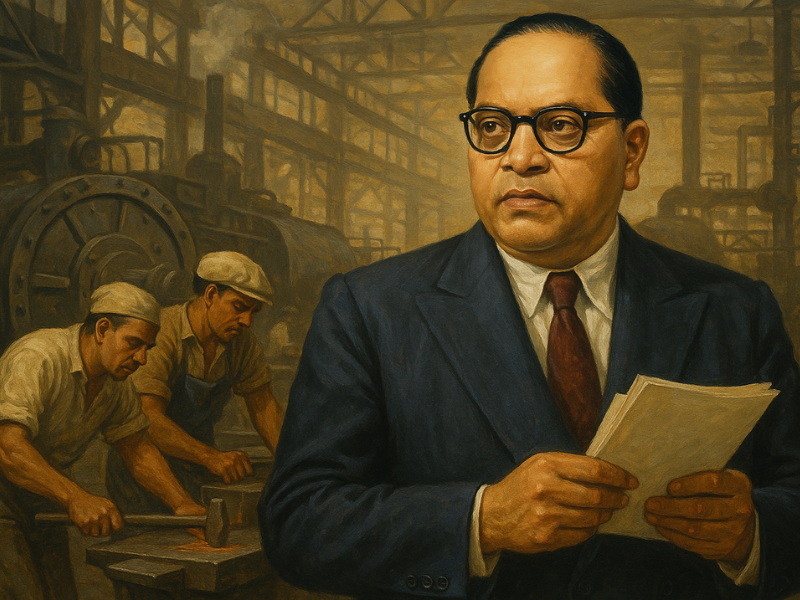
Dr. B.R. Ambedkar remains one of the most influential thinkers of modern India. His contributions to the Constitution, the struggle against caste discrimination, and the fight for social equality continue to inspire movements across the world. Beyond his legal mastery, Ambedkar championed a deeper philosophy—social democracy, a system where democratic values must exist not only in the political sphere but also in everyday social life.
In today’s India, marked by growing economic gaps, social tensions, and institutional challenges, Ambedkar’s vision offers direction, clarity, and hope.
What Ambedkar Meant by Social Democracy
Ambedkar famously stated that India must achieve a form of democracy where people “live in the spirit of liberty, equality, and fraternity.”
He believed:
- Political democracy alone is insufficient.
Elections, parliaments, and governments cannot guarantee dignity unless society itself practices equality. - Social and moral values are the true foundation of democracy.
Discrimination, hierarchy, and exclusion weaken democratic systems. - Democracy requires constant protection.
It must be nurtured through education, civic responsibility, and constitutional morality.
His understanding of democracy was not just institutional but fundamentally human-centered.
Why Ambedkar’s Social Democracy Matters Today
1. Rising Social Inequality
India continues to face deep inequalities—economic, caste-based, gender-based, and regional. Ambedkar warned that inequalities in society could turn political democracy into a “top dressing on an undemocratic soil.”
Today, his warning feels more relevant than ever. Sustainable development requires equality in opportunities, justice, and human dignity.
2. Challenges to Constitutional Values
The Constitution stands as Ambedkar’s greatest gift to India. But increasing polarization and disregard for rights-based governance threaten its spirit. Ambedkar stressed the importance of constitutional morality—respecting constitutional ideals even when inconvenient.
In a world of rapidly shifting political power, his message reminds us that democracy survives only when citizens protect their freedoms proactively.
3. Caste-Based Violence and Discrimination
Despite legal reforms, caste violence, manual scavenging, unequal access to education, and discrimination persist. Ambedkar’s call to “annihilate caste” remains essential to creating a just society.
Movements across India and abroad now draw inspiration from his philosophy to challenge oppressive structures and empower marginalized communities.
4. Global Human Rights Movements
Ambedkar has become a global symbol of social justice. His teachings resonate in Africa, Europe, Japan, and North America, where activists see him as a champion of human dignity and equality.
The rise of global Ambedkarite festivals, academic conferences, and research networks shows that his thought is shaping international conversations on democracy and human rights.
Ambedkar’s Message for Young India
Educate
Education was, for Ambedkar, the key to empowerment. In an era of misinformation and social media influence, his call for critical thinking is indispensable.
Agitate
He encouraged peaceful resistance against injustice. Modern youth movements on gender equality, environment, and human rights echo his philosophy.
Organize
Ambedkar believed in collective action. Social transformation is possible only when communities stand together with purpose and discipline.
Building a Social Democratic Future
Ambedkar’s vision is not a philosophical idea—it is a roadmap for India’s progress. To truly honor him, society must work toward:
- Equal access to education and opportunities
- Removing caste-based barriers
- Protecting constitutional rights
- Promoting gender justice
- Strengthening democratic institutions
- Encouraging rational and scientific thinking
Ambedkar wanted Indians to think of themselves as equal citizens bound by fraternity—a value the nation needs more than ever.
Conclusion
Dr. B.R. Ambedkar’s concept of social democracy remains timeless. It challenges us to look beyond political structures and focus on human dignity, justice, and equality in everyday life. As India navigates complex social and political transitions, Ambedkar’s wisdom provides guidance rooted in compassion, reason, and constitutional morality.
His message is simple yet transformative:
Democracy thrives only when every human being is treated with dignity.